How Are Visualization And Urban Planning Being Transformed By 3D Printing?

Now that 3D printing technology has advanced, the whole field of urban planning and designing has been revolutionised. This creative method is gradually articulating how planning, designing, and even visualising their cities should be done. Stakeholder engagement can be enhanced, models made more accurate, and more effective cities of the future built by embracing the use of 3D printing by urban planners.
Transformative Technology: 3D Printing for Urban Planning
For many years, urban planners have presented their concepts and recommendations using conventional techniques. Nonetheless, 3D printing has become a potent instrument with several benefits over traditional methods. With the use of this technology, metropolitan landscapes, structures, and infrastructure can be replicated in great detail on tangible media.
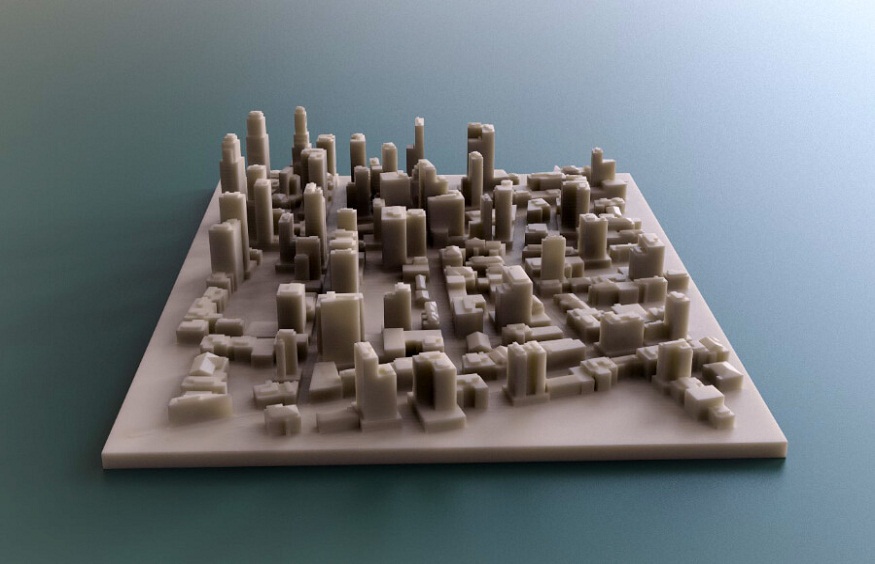
Generating accurate, scaled models of entire neighbourhoods or cities is one of the main advantages of 3D printing for urban planning. It is simpler for planners, architects, and decision-makers to see and assess many design possibilities when planned developments are represented in concrete form by these models.
First, digital designs or scans of the existing locations are usually used to start the process of 3D printing models for urban planning. A format that is compatible with 3D printers is then created from these digital data. Next, using materials like plastic, resin, or even more environmentally friendly choices like recycled materials, the printer constructs the model layer by layer.
Simplifying the Process of Designing
The design process for architects and urban planners is also made easier by 3D printing technology. Designers can swiftly and effectively generate several versions of their plans rather than having to spend weeks or months manually building physical models. Quick design changes and in-depth concept investigation are made possible by this quick prototyping capability.
Intricate details and complicated geometries that would be difficult or impossible to create with conventional model-making procedures can also be created with 3D printing. Efficient planning of big urban developments and local revitalization greatly benefit from this degree of precision and detail.
3D Printing Devices Integrated into Urban Infrastructure
Urban planning can benefit from 3D printing’s uses beyond visualisation, even if it is generally connected with models and prototypes. Urban infrastructure functional components, such as 3D-printed gears, are currently being produced using this technology.
Traffic control systems, public transportation systems, and even infrastructure maintenance in cities can all benefit from the usage of 3D-printed gear. Over conventional production techniques, these custom-made gears have the following benefits:
Personalization: Using three-dimensional printing, gears with precise measurements and characteristics can be made for certain urban uses. Better and longer-lasting mechanical systems could result from this personalization for the entire city.
Expense-effectiveness: 3D printing gears can be less expensive than conventional manufacturing techniques for small-scale production or replacement parts. Maintaining outdated infrastructure or developing specialised elements for urban development are two areas where this is especially helpful.
Speedy prototyping: 3D printed gears allow for speedy iteration and testing of various designs for creating new urban systems or enhancing current ones. Greater innovation and efficiency in urban solutions may result from this process of development’s adaptability.
Sustainability: By generating equipment locally and on-demand, 3D printing can lessen the need for big stocks and long-distance shipping, which can help promote more environmentally friendly urban planning techniques.
A prime example of how this technology is changing not just the planning and visualisation parts of urban development but also the actual elements that keep cities running is the incorporation of 3D-printed gears into urban infrastructure.
Visualizing Designs in Three Dimensions Using 3D Architecture
Within the field of urban planning, architectural visualisation is one of the most notable applications of 3D printing. Conventional architectural illustrations, however valuable, frequently fail to capture the real spirit of a suggested design. By producing concrete, three-dimensional models of architectural ideas, 3D printing closes this disparity.
Now, individual structures or entire city blocks may be modelled in great detail using 3D printing by architects and urban planners. Intricate aspects like landscaping, facade detailing, and even interior layouts can be included in these models. In various respects, being able to create such intricate visualisations is beneficial.
Evaluation of the design: When exposed to and handling a physical model, architects and clients are better able to evaluate the functional and aesthetic aspects of a design. The design process can often be improved and insightful discoveries are made with this hands-on approach.
Public engagement: 3D architectural visualization models have the potential to pique public interest and comprehension when new urban development concepts are introduced. Seeing precise, scaled-down representations of the plans makes it easy for people to understand the scope and significance of the suggested community changes.
Marketing and promotion: 3D printed models are an effective marketing tool for large-scale urban development initiatives. Through the use of 3D scanning and virtual reality platforms, they can even be shared online and exhibited in tourist centres and promotional materials.
Historical preservation: By using 3D printing, precise copies of architectural parts can be produced in situations when urban planners are attempting to restore or preserve historical sites. In addition to being useful as teaching aids in museums and history centres, these reproductions can support restoration projects.
The more advanced the technology becomes, the more detail that can be achieved with architectural models that are 3D printed. To further improve the realism and practicality of these representations, certain 3D printers can now create models with colour, texture, and even transparency.
Challenges and Future Prospects
In addition to its many advantages, 3D printing has certain drawbacks for urban planning and visualization. For smaller planning offices or towns, access to high-quality 3D printers and materials may be restricted due to their considerable cost. Knowing how to use 3D printing technology to enhance current urban planning operations comes with a learning curve.
Technology integration: By combining virtual and augmented reality with 3D printing, it is possible to produce immersive presentations and public consultations for urban planning.
Sustainable materials: The creation of environmentally friendly 3D printing materials may further integrate technology with the objectives of sustainable urban development, particularly as environmental concerns gain ground.
Automated urban analysis: It is possible to create “smart” physical models that offer real-time information about urban dynamics by integrating sensors and data processing tools with 3D printed models.
Conclusion
Design, development, and understanding of cities are changing as a result of the use of 3D printing in urban planning and visualisation processes. Technology has proven to be a useful tool for city authorities, architects, and urban planners. It may be used to produce functioning components like 3D-printed gears or create precise architectural models.
The influence of 3D printing on urban planning is only going to increase as technology develops. In urban development projects, improved communication, teamwork, and decision-making are being fostered by the technology’s capacity to provide precise, tangibly represented urban areas and architectural designs.